In this article the different tags and data types of the Data Collection Module are explained.
Tags show if data points are mandatory or voluntary and if there are future changes to the disclosure requirements and respective data points.
Tags are shown on the Data Collection Overview Page as Icons. If you hover over the tag a short description is shown:
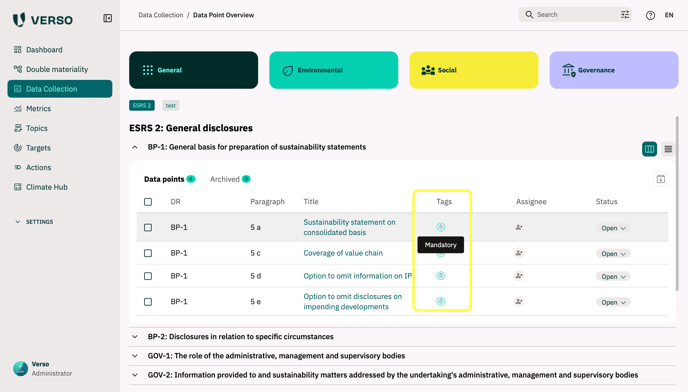
There are also visible on the Data Point Detail Page:
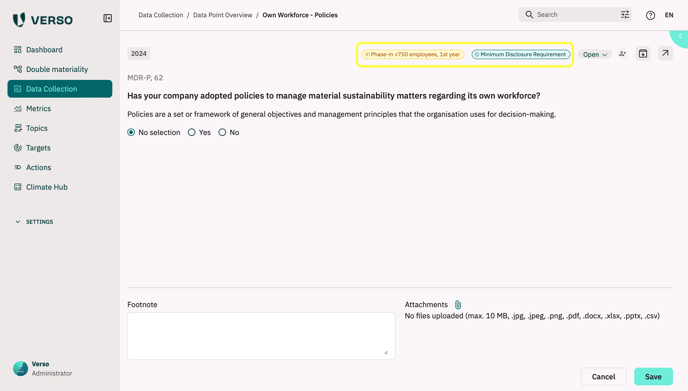
To differentiate between the different disclosure requirements a number of different tags are used. Sometimes also multiple tags are assigned to one data point:
Mandatory
If a Data Point has the tag ‘Mandatory’ it means that data has to be disclosed no matter e.g. the company size or other aspects. Usually the wording of ‘shall disclose’ is used in the regulation and on our platform to mark the related data points.
Voluntary
Some data points are voluntary meaning that they do not have to be but can be disclosed. This is to encourage good practice in terms of transparency. Usually the wording of ‘may disclose’ is used in the regulation and on our platform to mark the related data points.
Minimum Disclosure Requirement
A minimum disclosure requirement tag specifies that certain data points and content have to be disclosed when reporting on polices, actions or targets either in accordance with a disclosure requirement (ESRS) or for company-specific topics.
Phase-in Tags
Companies that have to prepare a CSRD sustainability report are given a certain amount of relief or postponement with the phase-in regulations of the ESRS. The transitional periods make it possible to address certain topics at a later date. That means that some disclosure requirements will be gradually introduced. We use a number of tags to show the different phases.
Phase-in all companies, 1st year
No information needs to be provided for this data point in the first year for all companies.
Phase-in <750 employees, 1st year
No information needs to be provided for this data point in the first year for companies with < 750 employees (e.g. ESRS E1-6 or ESRS S1).
Phase-in <750 employees, 2 years
No information needs to be provided for this data point in the first two years for companies with < 750 employees (e.g. ESRS S2).
Phase-in all companies, 3 years
No information needs to be provided for this data point in the first year for all companies. In addition, qualitative information is sufficient in the first three years (e.x. ESRS E3-5).
For more detailed info on the phase-in regulations refer to our article: ![]() Phase-in-Regelungen der ESRS: Alles über die Übergangsfristen beim CSRD-Bericht
Phase-in-Regelungen der ESRS: Alles über die Übergangsfristen beim CSRD-Bericht
No Tag
Some data points may not have a tag displayed. For those data points it depends on the materiality if companies have to provide further inside. Companies always have to give information if the topic and disclosure requirement is material to them and the data point is material to the objective of the disclosure requirement.
They can decide whether to give further information if:
-
the topic is not material (some exceptions apply)
-
the disclosure requirement is not material
-
the data point is not material to the objective of the disclosure requirement (some exceptions apply)
There is also the possibility that the data point question cannot be answered because what is asked does not apply to the company or there are no information available. If companies do not have (enough) information to answer a question (precisely) this should be disclosed and made transparent.
It is recommended that the reason for not providing information (e.x. does not apply) on a data point is always recorded in the footnotes / comments on the Data Point Detail Page so that e.x. auditors have access to important background knowledge. Afterwards data points can be archived.
Overall it is recommended to give as much transparent information as possible even if a data point does not seem to be material to a company’s business model and / or value chain.
Tags for VSME
When reporting under the VSME, following tags are used due to the structure of the standard:
Mandatory
If a Data Point has the tag ‘Mandatory’ it means that data has to be disclosed. Usually the wording of ‘shall disclose’ is used in the standard to mark the related data points.
Voluntary
Some data points are voluntary meaning that they do not have to be but can be disclosed. Usually the wording of ‘may disclose’ is used in the standard to mark the related data points.
If applicable
Some datapoints are to be reported only ‘if applicable’ to the undertaking’s circumstances. The “if-applicable “approach is used in the VSME, as within the VSME standard a double-materiality analysis is not required.
If applicable + voluntary
Some data points are marked with the tags ‘If applicable’ + ‘voluntary’. This means that the information must initially only be considered if it is applicable to the undertaking’s circumstances. However, it is then still a voluntary data point and the undertaking can provide the information voluntarily.
For example, the data points in B1, Guidance 79 only need to be answered if the undertaking is a cooperative, and if so, they can be answered voluntarily.
No Tag
All data points that originate directly from the VSME carry one or multiple tags. If a VSME data point does not carry a tag, it has been added to the platform by VERSO for better guidance. These are data points from which further dependent data points emerge, depending on the response. Therefore, these should always be answered.
Other tags, such as
- Phase-in periods and
- Minimum disclosure requirements
from the ESRS are not used in the VSME.
Data Types
In order to disclose all data in an appropriate way there are different data types included in the Data Collection. Depending on the required information the provided questions will ask the users to disclose their data in a certain way. There are quantitative as well as qualitative data types and mixed forms.
Quantitative data types
For all quantitative data types a single numerical value can be entered.
Example single value - data type: percentage

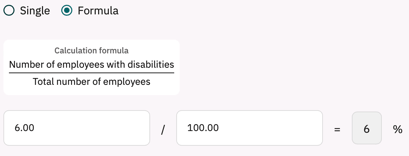
For some data types we provide the option of using a formula with multiple input fields to calculate the needed value within our software.
Example formula - data type: percentage
The following quantitative data types exist:
-
percentage
-
monetary / monetary range
-
decimal
-
area
-
energy
-
emissions
-
intensity
-
mass
-
rate
-
volume
-
integer
There are also other data types that are non-numerical but comparable. In ESRS they are defined as semi-narrative.
These are:
-
date
-
year
-
boolean (choice between two options, e.x. Yes/No)
-
enumeration (choice between multiple options)
Additionally, one qualitative data type is provided:
-
textbox
Metrics can be seen as an additional, more complex data type. Some tables require quantitative data while others ask for qualitative information.
